half life formula pharmacology
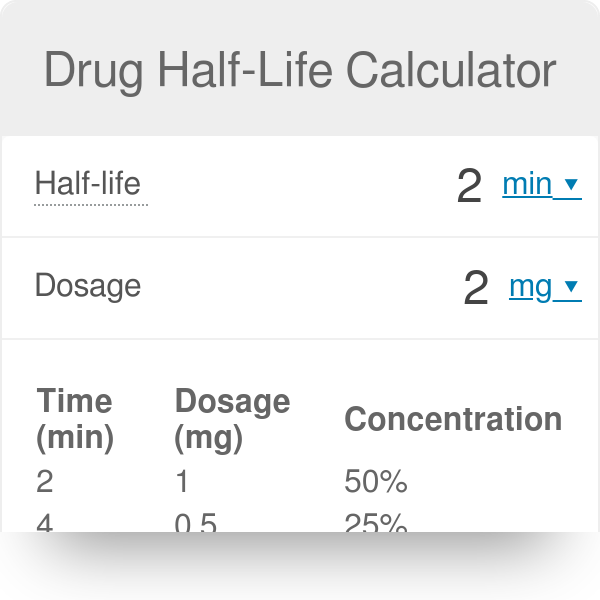
Half-life t½ is the time required to reduce the concentration of a drug by half. T - time that has passed since the first original administration of the drug.

Elimination Half Life An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Half-life is the time required for the amount of something to fall to half its initial value.

. Math Calculations in Pharmacology. It means the more the drug is distributed in the body the more the half-life is. The formula for half life is t 1 2 l n 2 λ 0693 λ.
The half-life of a drug is the time taken for the plasma concentration of a drug to reduce to half its original value. Authors H Boxenbaum 1 M Battle. Half-Life in Pharmacology Quiz.
Apparent half-life t 12. N t N0. After 1 half-life you will have reached 50 of steady state.
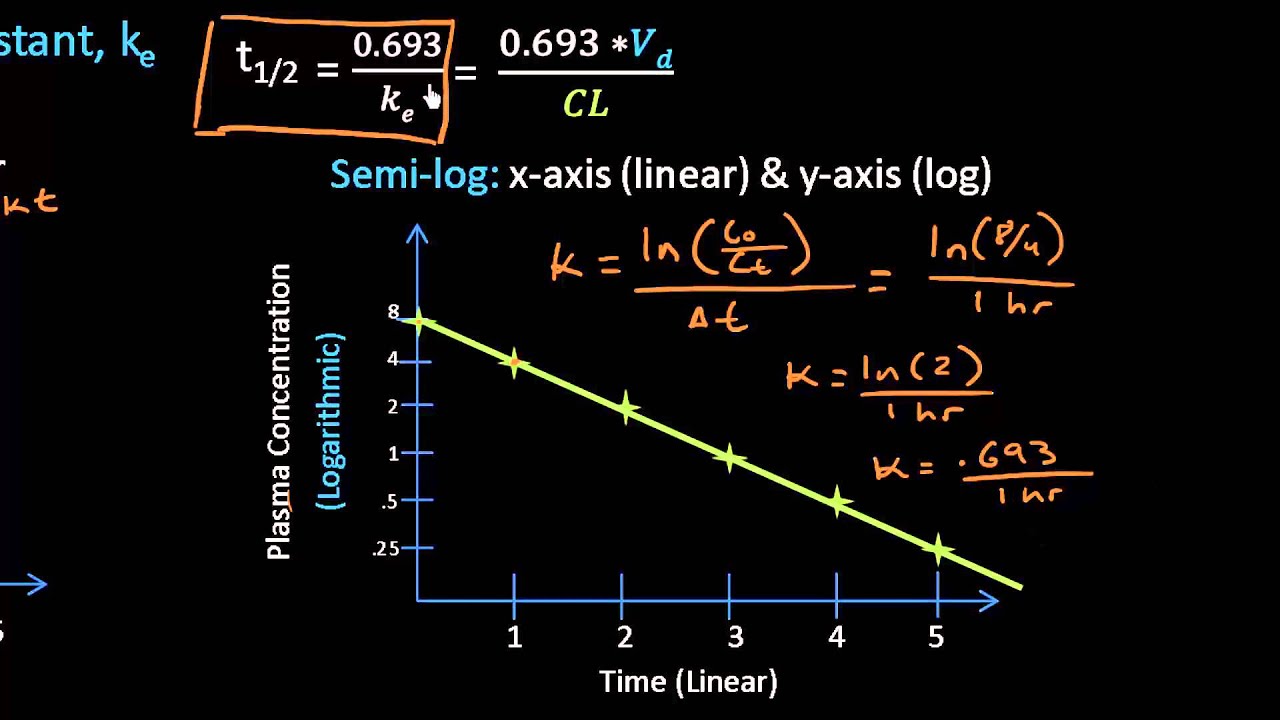
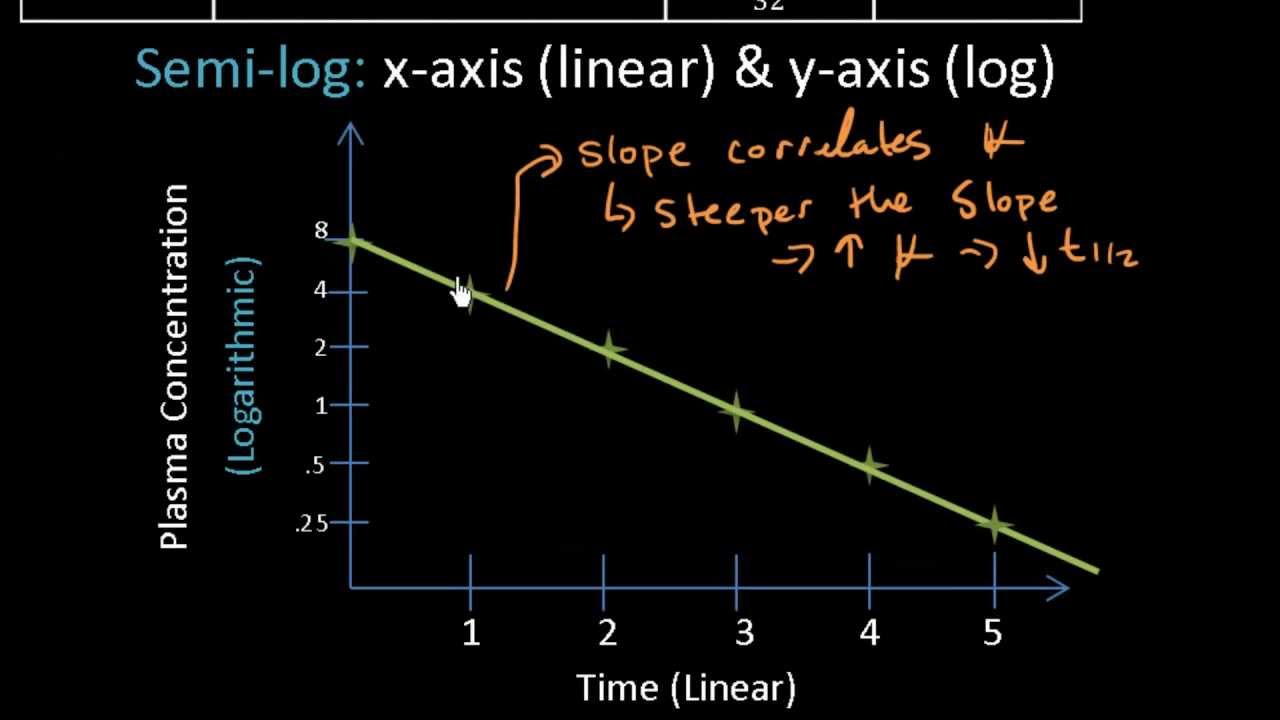
Clearance refers to the process. λ is the slope of the plasma concentration-time line on a logarithmic y scale. A pharmacological definition and an analysis to its formula.
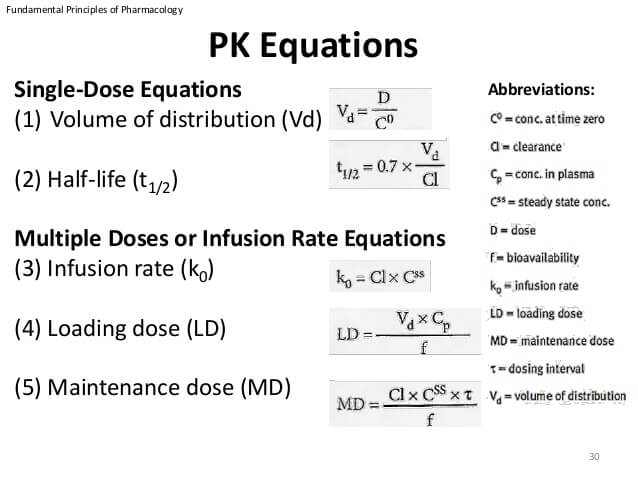
The half life of a medication is the amount of time it takes for the concentration of that medication in a persons blood to be reduced by one half. The formula for half-life is t½ 0693 Vd CL Volume of distribution Vd and clearance CL are required to calculate this variable. Formula half life 0693 ke half life 0693 0015 462 hours so this means that the drug will take 462 hours to remove roughly half of the drugs concentration in the body.
So if you take ambien after 2 hours the plasma concentration will. T 1 2 ln 2 V D C L displaystyle t_frac 12frac ln 2cdot V_DCL. The formula for half-life is t½ 0693 Vd CL Volume of distribution Vd and clearance CL are required to calculate this variable.
Formulas. The measurement of this quantity may take place in grams moles number of atoms etc. For drugs with first order kinetics this is a constant.
Effective half-life in clinical pharmacology. Half-life t½ is the time required to reduce the concentration of a drug by half. Affiliation 1 Wyeth.
Inversely proportional to the fraction of the dose lost in each dosing interval. Accumulation factor 1Fraction lost in one dosing interval 11 - fraction remaining For example the accumulation factor for a drug given once every half-life. Dosaget - the amount of drug present in a patients body after time t.
N t N0. N t N0. In some cases such as for controlled-release preparations the rate of decline of the drug plasma.
K first order rate constant. Where N0 refers to the initial quantity of the substance that will decay. Dosaget Dosage0 05 tT Where.
In this lesson we will define what a half-life is in pharmacological terms and explain how it is relevant. The converse of half-life is doubling time. Fractional rate of drug removal from the body.
Effective half-life in clinical pharmacology. Half-life t 12 1. Half-life is used to estimate how long it takes for a drug to be removed from your body.
This rate is constant in first-order kinetics and is independent of drug concentration in the body. By definition t 12 is the time required for the concentration to fall by one half. Half-life allows the calculation of the time required for plasma concentrations to reach steady-state after starting or changing a dosing regimen.
Pharmacokinetics Mnemonics Epomedicine Half Life Deranged Physiology Half Life Deranged Physiology Pharmacokinetics Vd Clearance Half Life Calculation Drug Distribution Elimination Rate Youtube. Pharmacology drug half life practice questions. The mathematical representation of Half life is given below.
T - the half life of a drug. The formula for half-life is t½ 0693 Vd CL Volume of distribution Vd and clearance CL are required to calculate this variable. Margin of Safety in Pharmacology.
The constant 07 in equation 6 is an approximation to the natural logarithm of 2. T12 0693Volume of distributionClearance or. The half-life of Ambien is about 2 hours.
Effective half-life in clinical pharmacology J Clin Pharmacol. What is half life in pharmacokinetics. Our drug elimination half life calculator uses the following equation.
See the video below for more details. Elimination rate constant λ. Half-life is useful because it indicates the time required to attain 50 of steady stateor to decay 50 from steady-state conditionsafter a change in the rate of drug administration.
Half life formula pharmacology Thursday March 17 2022 Edit. The formula for half-life is. The formula for half-life is t½ 0693 Vd CL Volume of distribution Vd and clearance CL are required to calculate this variable.
Math Calculations in Pharmacology. One can describe exponential decay by any of the three formulas. Half-life t½ is the time required to reduce the concentration of a drug.
Formula Half Life 0693 KE Half Life 0693 0015 462 hours So this means that the drug will take 462 hours to remove roughly half. The half-life is directly proportional to the volume of drug distribution. Half-life is determined by clearance CL and volume of distribution V D and the relationship is described by the following equation.
This rate is constant in first-order kinetics and is independent of drug concentration in the body. Heres the formula for half-life. Half life formula half life equation Half life 0693k.
Half Life Pharmacology Flashcards Draw It To Know It

Elimination Rate Constant An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
First Order Elimination Rate Constant And Half Life A Closer Look Lect 11 Youtube

Animated Plasma Half Life Half Life Pharmacology Pharmacokinetics Youtube
Loading Dose Pharmacology Flashcards Draw It To Know It
Drug Half Life An Overview Pharm Lect 10 Youtube

Elimination Rate Constant An Overview Sciencedirect Topics